A Guide to Double Declining Balance Depreciation Method

Also, note that the expense in the fourth year is limited to the amount needed to reduce the book value to the $20,000 salvage value. Thus, an increase in the cost of repairs of each subsequent year is compensated by a decrease in the amount of depreciation for each subsequent year. In the second year, depreciation how to claim the property tax deduction is calculated in a regular way by multiplying the remaining book value of $36,000 ($40,000 — $4,000) by 40%. Residual value is considered only in the last year of the asset’s life. This is when that year’s depreciation is limited to the amount that will reduce the asset’s book value to its residual value.
Double Declining Balance Method for Depreciation (With Examples)
If you want to learn more about fixed asset accounting as a whole, then head to our guide on what fixed asset accounting is, where we discuss the four important things you need to know. Also, if you want to know the other essential bookkeeping tasks aside from fixed asset accounting, you can read our piece on what bookkeeping is and what a bookkeeper does. Let’s assume that FitBuilders, a fictitious construction company, purchased a fixed asset worth $12,500 on Jan. 1, 2022. The company estimates that its useful life will be five years and its salvage value at the end of its useful life would be $1,250. The Units of Output Method links depreciation to the actual usage of the asset. It is particularly suitable for assets whose usage varies significantly from year to year.
Pros of the Double Declining Balance Method
By contrast, the opposite is true when applying the straight-line method, the unit-of-production method, and the sum-of-the-years-digits method. Because the book value declines as the asset ages and the rate stays constant, the depreciation charge falls each year. Depreciation for an asset with a five-year expected life would span over six tax years, with a portion of a year’s deduction in year one and six. Since it is so widely used, and simple to understand, I go into great detail and provide examples in that tutorial. This formula is called double-declining balance because the percentage used is double that of Straight-line.
How to calculate Depreciation
Our intuitive software automates the busywork with powerful tools and features designed to help you simplify your financial management and make informed business decisions. Our team is ready to learn about your business and guide you to the right solution. In many countries, the Double Declining Balance Method is accepted for tax purposes. However, it is crucial to note that tax regulations can vary from one jurisdiction to another. Therefore, businesses should verify the specific tax rules and regulations in their region and consult with tax experts to ensure compliance.
Certain fixed assets are most useful during their initial years and then wane in productivity over time, so the asset’s utility is consumed at a more rapid rate during the earlier phases of its useful life. (You can multiply it by 100 to see it as a percentage.) This is also called the straight line depreciation rate—the percentage of an asset you depreciate each year if you use the straight line method. The beginning book value is the cost of the fixed asset less any depreciation claimed in prior periods. Under the DDB method, we don’t consider the salvage value in computing annual depreciation charges.
The Double Declining Balance Method (DDB) is a form of accelerated depreciation in which the annual depreciation expense is greater during the earlier stages of the fixed asset’s useful life. The double declining balance depreciation method shifts a company’s tax liability to later years when the bulk of the depreciation has been written off. The company will have less depreciation expense, resulting in a higher net income, and higher taxes paid.
At Finance Strategists, we partner with financial experts to ensure the accuracy of our financial content. For information pertaining to the registration status of 11 Financial, please contact the state securities regulators for those states in which 11 Financial maintains a registration filing. This rate is applied to the asset’s remaining book value at the beginning of each year. Insights on business strategy and culture, right to your inbox.Part of the business.com network.
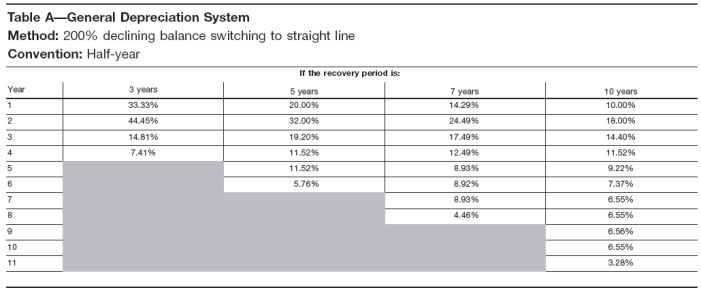
In the last year of an asset’s useful life, we make the asset’s net book value equal to its salvage or residual value. This is to ensure that we do not depreciate an asset below the amount we can recover by selling it. Another thing to remember while calculating the depreciation expense for the first year is the time factor. Unlike the straight-line method, the double-declining method depreciates a higher portion of the asset’s cost in the early years and reduces the amount of expense charged in later years. For example, if an asset has a useful life of 10 years (i.e., Straight-line rate of 10%), the depreciation rate of 20% would be charged on its carrying value.
- Depreciation is a complicated business and I hope my tutorials give you a good grasp as to how assets are expensed in the accounting system.
- In contrast to straight-line depreciation, DDB depreciation is highest in the first year and then decreases over subsequent years.
- IRS Publication 946 goes into great detail as to the various ways to handle this situation.
- Imagine being able to maximize your tax deductions and improve your cash flow in the initial years of an asset’s life.
- Depreciation is the process of allocating the cost of a tangible asset over its useful life.
He is a CFA charterholder as well as holding FINRA Series 7, 55 & 63 licenses. He currently researches and teaches economic sociology and the social studies of finance at the Hebrew University in Jerusalem. So, in the first year, the company would record a depreciation expense of $4,000. As a result, at the end of the first year, the book value of the machinery would be reduced to $6,000 ($10,000 – $4,000).
Multiply this rate by the asset’s book value at the beginning of each year to find that year’s depreciation expense. Double declining balance depreciation is an accelerated depreciation method that charges twice the rate of straight-line deprecation on the asset’s carrying value at the start of each accounting period. The declining balance method is one of the two accelerated depreciation methods and it uses a depreciation rate that is some multiple of the straight-line method rate.
It is important to note that we apply the depreciation rate on the full cost rather than the depreciable cost (cost minus salvage value). Therefore, it is more suited to depreciating assets with a higher degree of wear and tear, usage, or loss of value earlier in their lives. To create a depreciation schedule, plot out the depreciation amount each year for the entire recovery period of an asset.